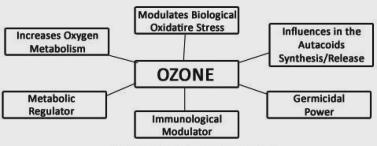
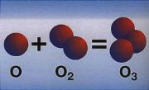
WHAT IS OZONE?
Ozone
is
a
particular
form
of
oxygen.
There
are
molecules
with
two
atoms
in
the
normal
atmospheric
oxygen,
but
the
ozone
contains
one
oxygen
molecule
with
three
different
values.
So
the
ozone
can
be
dissolved
quickly
about
15
times more than the oxygen in the blood.
We have to introduce a right concentration in the body due that the effect of ozone administration at a smaller
concentration
could
be
ineffective
and
a
higher
concentration
decrease
the
activity
of
antioxidant
defence
system
and
could
possibly
have
harmful effects.
Oxygen + Energy = OZONE
More Oxygen in the cell means more Energy.
THE IMPORTANCE OF OXYGEN
Healthy
cells
in
the
body
need
and
love
oxygen.
Most
undesirable
micro-organisms
are
anaerobic,
which
means
that
they
thrive
in
the
absence
of
oxygen;
in
fact,
they
are
destroyed
by
the
presence
of
oxygen.
Organisms
such
as
fungi,
parasites,
bacteria,
and
primitive
viruses
like
HIV,
Epstein
Barr,
Coxsackie
and
Cytomegalovirus
are
often
associated
with
states
of
ill
health.
Note
that
conventional
medicine blames these micro-organisms for many chronic illnesses.
The
body
becomes
deprived
of
adequate
levels
of
oxygen
through
improper
breathing,
polluted
air,
inadequate
nutrition
and
junk
foods,
and stress. This provides an anaerobic environment in which the micro-organisms thrive.
Healthy
cells
which
have
sufficient
oxygen
and
nutrients,
manufacture
an
enzyme
coating
around
themselves
which
protects
them
against
invasion.
Oxygen
starved
cells
are
unable
to
produce
enough
enzymes
to
fortify
their
cell
walls;
they
subsequently
become
weaker
and
more vulnerable.
In
addition,
cancer
begins
when
a
normal
cell
cannot
get
enough
oxygen.
If
the
level
of
available
oxygen
falls
below
60%,
a
cancer
response
is
triggered
in
the
cells.
In
order
to
survive
the
cell
begins
to
ferment
sugar
instead
of
burning
it.
This
results
in
a
greatly
reduced
energy
output,
which
means
that
a
proper
enzyme
coating
cannot
be
maintained
around
the
cell.
The
restriction
on
cell
replication
is
inactivated, and the cell begins to make copies of itself wildly.
Heat
is
continually
generated
through
the
chemical
action
of
oxygen
upon
carbon,
which
releases
carbon
dioxide
for
elimination.
If
insufficient
oxygen
is
present,
carbon
monoxide
is
produced
instead.
Carbon
monoxide
is
an
irritant
to
the
nervous
system,
interferes
with
organ
functions,
reduces
basal
body
temperature,
and
prevents
oxygen
uptake
by
the
red
blood
cells.
This
has
the
effect
of
debilitating
the
body, thus making it susceptible to infection and disease.
HOW DOES OZONE WORK?
1.- Inactivation of bacteria, viruses, fungi, yeasts and protozoa
Ozone
has
been
shown
to
destroy
the
outer
shell
of
most
micro-organisms,
thereby
penetrating
the
cell
membrane
and
altering
the
DNA.
Sophisticated
organisms
such
as
human
cells
have
enzymes
that
can
restabilise
disrupted
DNA,
whereas
primitive
organisms
do
not
have
this
protective
capability.
This
is
another
mechanism
by
which
ozone
selectively
targets
disease
causing
micro-organisms,
and
spares
healthy cells.
Repeated
treatments
of
ozone
therapy
are
usually
needed,
because
certain
viruses
and
fungi
are
more
susceptible
at
certain
stages
of
their
development.
Some
micro-organisms
are
much
more
resistant
than
others,
and
will
require
more
treatment.
The
viruses
that
contain
lipids
are
more
sensitive
to
deactivation
by
ozone
–
Herpes,
Mumps,
Measles,
Influenza,
Rabies,
HIV
and
the
Chronic
Fatigue
producing
viruses: Epstein Barr, Coxsackie and Cytomegalovirus.
2.- Stimulation of oxygen metabolism
Ozone
causes
increased
metabolism
inside
the
red
blood
cells
[increased
2,3-DPG],
which
releases
more
oxygen
to
the
tissues.
Ozone
also
stimulates
the
production
of
enzymes,
which
act
as
cell
wall
protectors
and
scavengers
of
free
radicals.
It
enhances
energy
production
in
the cells by complex biochemical reactions.
3.- Formation of Peroxides
When
ozone
is
introduced
into
the
body,
it
is
broken
down
into
free
radical
agents
called
peroxides.
These
have
beneficial
effects
because
they
are
attracted
to
weakened
or
diseased
cells
and
react
with
lipids
[fats]
in
the
cell
membrane.
The
enzymes
in
the
healthy,
intact
cell
wall
prevent
penetration
by
these
peroxides.
Thus
the
peroxides
in
ozone
selectively
attack
only
those
cells
which
contain
parasites,
viruses etc, or are weakened by cancer or toxins.
4.- Enhancement of circulation
In
circulatory
disease,
a
clumping
of
red
blood
cells
hinders
blood
flow
through
the
small
capillaries
and
decreases
oxygen
uptake
by
the
red
blood
cells
due
to
reduced
surface
area.
Ozone
reduces
or
eliminates
clumping,
and
restores
flexibility
thereby
increasing
oxygen
carrying capacity. Improved viscosity of the blood also leads to better oxygenation of the tissues.
Ozone
oxidises
the
plaque
in
arteries,
which
unclogs
and
frees
up
the
circulation.
A
vasodilator,
Prostacycline,
is
also
produced
by
ozone,
which dilates the arteries.
5.- Dissolution of tumours
Ozone inhibits cancer cell metabolism. In addition, ozone oxidises the outer lipid layer of cancer cells, thus destroying them.
6.- Activation of the immune system
Optimal
administration
of
medical
ozone
causes
an
increase
in
the
production
of
interferon
and
interleukins,
which
launch
an
entire
cascade of immunological reactions.
7.- Effect on medicines
The
potency
of
any
medicine
taken
concurrently
with
ozone
treatment
is
greatly
increased.
The
unpleasant
side
effects
of
toxic,
but
necessary, medications such as chemotherapy can be greatly minimised by ozone therapy.
WHAT CAN OZONE DO?
Inactivates viruses, bacteria, yeasts, fungi and protozoa
Stimulates the immune system
Improves circulation, clearing arteries and veins
Purifies blood and lymph
Normalizes hormone and enzyme production
Reduces inflammation
Reduces pain and calms the nerves
Prevents stroke damage
Improves cardiac arrhythmias
Improves brain function and memory
Oxidises toxins, allowing their excretion
Chelates heavy metals
Prevents and reverses degenerative disease
Prevents and treats communicable diseases
Prevents and treats Autoimmune disease
Increases the potency and minimizes the side effects of chemotherapy
Assist in treatment of cancers, post viral Chronic Fatigue Syndromes, Autism, etc.
FIELDS OF APPLICATION. INDICATIONS
Surgery
Abscesses,
wound
infection,
septic
conditions,
peritonitis,
decubitis,
burns,
badly
healing
wounds,
trophic
ulcers,
chronic
osteomyelitis,
thrombophlebitis,
arterial
occlusive
disturbances
of
the
lower
limbs,
diabetic
foot,
purulent-destructive
lung
&
pleura
diseases,
purulent
arthritis, deformating arthrosis, cardio-surgical interferences, pre- and postoperative treatment.
Internal medicine
Chronic
gastritis
&
gastroduodenitis,
chronic
colitis,
peptic
ulcer,
chronic
hepatitis,
hepatocirrhosis,
chronic
bronchitis,
bronchial
asthma,
rheumatic diseases, arthritis & arthrosis, ischemic heart disease, allergic diseases, diabetes mellitus
Urology
Chronic pyelonephritis, acute and chronic renal failure (nephrism), cystitis, diseases transmissible by sexual way, urethritis, prostatitis
Neurology
Ischemic
apoplectic
attack,
cerebrovascular
insufficiency,
diseases
of
peripheral
nervous
system,
migraine,
disseminated
sclerosis,
compressive ischemic neuropathies, spinal osteochondrosis
Obstetrics & Gynecology
Inflammatory
female
genital
diseases,
bacterial
vaginosis,
vulvar
dystrophy,
gestosis,
early
toxicosis,
fetoplacental
insufficiency,
pregnancy
anemia,
spontaneous
&
threatened
abortion,
prevention
of
intrauterine
fetus
infection,
fatness-associated
pregnancy
complications,
infertility
Dermatology
Furunculosis,
pyoderma,
herpes,
mycosis,
scleroderma,
psoriasis,
neurodermatitis,
eczema,
bullous
dermatosis,
acne,
allergodermia,
agiitis, lichen planus, pemphigus etc.
Cosmetology
Acne rash, cellulites, local lipodystrophy, alopecia, vascular defects, hypertrophic & keloid scars, age related changes
Dentistry
Caries
lesions,
hypersensitive
teeth,
cracked
tooth
syndrome,
peri-apical
lesions,
gingival
&
periodontal
diseases,
post-extraction,
post-
extraction alveolitis, surgical procedures, peri-implantitis, soft-tissue lesions etc.
Ophthalmology
Blepharitis,
pain
syndrome,
eversion
of
the
eyelid,
glaucoma,
ischemia
of
the
eye
ground,
cataract,
keratitis,
conjunctivitis,
pemphigus,
erosion of the cornea, ulcers of the retina, hordeolum etc.
HOW IS IT ADMINISTERED?
1.- Intravenous therapy
An
intravenous
line
is
inserted
into
a
vein,
and
100-150ml
of
blood
is
drawn
into
a
sterile
vacuum
flask.
Medical
ozone
is
also
inserted
into
the
flask
and
when
the
two
are
rapidly
mixed
together,
the
blood
turns
a
bright
cherry
red.
This
ozonated
blood
is
now
highly
charged
with
oxygenating power, and fed back into the same vein. The whole procedure takes about 30 minutes.
2.- Vaginal, urethral or rectal insufflations
Ozone is introduced into the vagina, urethra or rectum by means of a catheter.
3.- Autohemotherapy
5-10 ml blood is withdrawn by syringe, mixed with ozone, and injected back into a deep muscle.
4.- External limb bagging
A limb is covered with an airtight bag and ozone is introduced into the bag for 30-40 minutes.
5.- Ozonated olive oil
Ozone
is
bubbled
through
olive
oil
continuously
for
7
days.
The
resulting
cream
is
very
effective
as
a
topical
application
in
a
wide
variety
of
skin conditions.
6.- Intramuscular, Intra-articular & intradiscal O2/O3 gas injections.
ARE THERE ANY PRECAUTIONS TO OBSERVE?
To
prevent
any
unwanted
oxidative
effects,
it
is
best
to
take
a
good
anti-oxidant
combination
for
7
days
before
starting
intravenous
ozone
therapy.
Ozone therapy
is contraindicated
in the following:
Acute
myocardial
infarction,
severe
cardiovascular
instability
(block,
Wolff-Parkinson-White),
convulsive
status,
pregnancy,
recent
internal
bleeding
and
blood
coagulation
disorder,
severe
anemia,
hyperthyroidism,
thrombocytopenia,
cramp
tendency,
ozone
allergy,
chronic
relapsing pancreatitis, alcoholic intoxication and Fauvism (a deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase).
References
Bocci, V. 2002. Oxygen-Ozone Therapy. A Critical Evaluation. Kluwer Academic Pub.
Bocci, V. 2005. Ozone, A new medical drug. Springer
Viehban-Haensler, R. 2002. The Use of Ozone in Medicine. 4th Ed. ODREI-Pub.
Viebahn-Hänsler, R. Ozon-Sauerstoff-Therapie. Editorial Haug. 2009.
Viebahn-Hänsler R. Hitos del ozono médico. Revista de la Sociedad Española del Dolor. Vol. 12. II. Editorial ARAN. 2005. 3-9.
Menéndez
Cepero
S.
A,
González
Álvarez
Ricardo,
Ledea
Lozano
O.E.
et
al.
Ozono:
Aspectos
básicos
y
aplicaciones
clínicas.
Editorial
CENIC.2008.
Rovira
G.
La
Ozonoterapia
tópica
en
el
manejo
de
úlceras
flebostáticas
dolorosas
de
más
de
seis
meses
de
evolución.
Rev.
Soc.
Esp.
Dolor 12: Nº Extra II, 48-52, 2005.
De
Lucas
J.C.
Infiltración
periférica
con
ozono.
Indicaciones,
técnicas
y
experiencia
clínica.
Revista
de
la
Sociedad
Española
del
Dolor.
Vol.12.II. Editorial ARAN. 2005. 37-47.
Hidalgo
Tallón
F.J.
Oxígeno-ozonoterapia:
una
realidad
médica.
Revista
de
la
Sociedad
Española
del
Dolor.
Vol.16.
3.
Editorial
ARAN.
2009. 190-191.
Andreula
C.,
Simonetti
L.,
et
al:
Minimally
Invasive
Oxygen-Ozone
Therapy
for
Lumbar
Disk
Herniation.
AJNR
Am
J
Neuroradiol
24:
996-1000, May 2003.
Baeza
J.
Infiltración
neuroaxial
con
ozono.
Fisiopatología
y
mecanismos
de
acción.
Revista
de
la
Sociedad
Española
del
Dolor.
Vol.12.
II. Editorial ARAN.2005. 18-23.
Bocci
V.
Mecanismos
de
acción
generales
de
la
ozonoterapia
y
mecanismos
en
el
tratamiento
del
dolor.
Revista
de
la
Sociedad
Española del Dolor. Vol.12. II. Editorial ARAN. 2005.24-36.
Borrelli
e.,
Bocci
V.
A
Novel
Therapeutic
Option
for
Crhonic
Fatigue
Syndrome
and
Fibromyalgia.
Riv
Ital
Ossigeno-Ozonoterapia
1:
149-153, 2002
If you would like additional information regarding our services or to request an appointment, you can contact us by phone
(952 80 53 68) or by
email
.









































© 2023 - Centro Medicina Natural y Antienvejecimiento - Neural therapy, Homeopathy, Ozone therapy, Carboxytherapy, Mesotherapy
Avda. Juan Carlos I, nº 29, portal 5, 2ºB -- 29680, Estepona (Málaga)


© 2023 - Centro Medicina Natural y Antienvejecimiento
Tel: 952 80 53 68
E-mail: info@medicinabiologica.es
Ozone Therapy
WHAT IS OZONE?
Ozone
is
a
particular
form
of
oxygen.
There
are
molecules
with
two
atoms
in
the
normal
atmospheric
oxygen,
but
the
ozone
contains
one
oxygen
molecule
with
three
different
values.
So
the
ozone
can
be
dissolved
quickly
about
15
times
more
than
the
oxygen in the blood.
We
have
to
introduce
a
right
concentration
in
the
body
due
that
the
effect of ozone administration at a smaller
concentration
could
be
ineffective
and
a
higher
concentration
decrease
the
activity
of
antioxidant
defence
system
and
could
possibly have harmful effects.
Oxygen + Energy = OZONE
More Oxygen in the cell means more Energy.
THE IMPORTANCE OF OXYGEN
Healthy
cells
in
the
body
need
and
love
oxygen.
Most
undesirable
micro-organisms
are
anaerobic,
which
means
that
they
thrive
in
the
absence
of
oxygen;
in
fact,
they
are
destroyed
by
the
presence
of
oxygen.
Organisms
such
as
fungi,
parasites,
bacteria,
and
primitive
viruses
like
HIV,
Epstein
Barr,
Coxsackie
and
Cytomegalovirus
are
often
associated
with
states
of
ill
health.
Note
that
conventional
medicine blames these micro-organisms for many chronic illnesses.
The
body
becomes
deprived
of
adequate
levels
of
oxygen
through
improper
breathing,
polluted
air,
inadequate
nutrition
and
junk
foods,
and
stress.
This
provides
an
anaerobic
environment
in
which
the micro-organisms thrive.
Healthy
cells
which
have
sufficient
oxygen
and
nutrients,
manufacture
an
enzyme
coating
around
themselves
which
protects
them
against
invasion.
Oxygen
starved
cells
are
unable
to
produce
enough
enzymes
to
fortify
their
cell
walls;
they
subsequently
become
weaker and more vulnerable.
In
addition,
cancer
begins
when
a
normal
cell
cannot
get
enough
oxygen.
If
the
level
of
available
oxygen
falls
below
60%,
a
cancer
response
is
triggered
in
the
cells.
In
order
to
survive
the
cell
begins
to
ferment
sugar
instead
of
burning
it.
This
results
in
a
greatly
reduced
energy
output,
which
means
that
a
proper
enzyme
coating
cannot
be
maintained
around
the
cell.
The
restriction
on
cell
replication
is
inactivated, and the cell begins to make copies of itself wildly.
Heat
is
continually
generated
through
the
chemical
action
of
oxygen
upon
carbon,
which
releases
carbon
dioxide
for
elimination.
If
insufficient
oxygen
is
present,
carbon
monoxide
is
produced
instead.
Carbon
monoxide
is
an
irritant
to
the
nervous
system,
interferes
with
organ
functions,
reduces
basal
body
temperature,
and
prevents
oxygen
uptake
by
the
red
blood
cells.
This
has
the
effect
of
debilitating
the
body,
thus
making
it
susceptible
to
infection
and
disease.
HOW DOES OZONE WORK?
1.-
Inactivation
of
bacteria,
viruses,
fungi,
yeasts
and
protozoa
Ozone
has
been
shown
to
destroy
the
outer
shell
of
most
micro-
organisms,
thereby
penetrating
the
cell
membrane
and
altering
the
DNA.
Sophisticated
organisms
such
as
human
cells
have
enzymes
that
can
restabilise
disrupted
DNA,
whereas
primitive
organisms
do
not
have
this
protective
capability.
This
is
another
mechanism
by
which
ozone
selectively
targets
disease
causing
micro-organisms,
and spares healthy cells.
Repeated
treatments
of
ozone
therapy
are
usually
needed,
because
certain
viruses
and
fungi
are
more
susceptible
at
certain
stages
of
their
development.
Some
micro-organisms
are
much
more
resistant
than
others,
and
will
require
more
treatment.
The
viruses
that
contain
lipids
are
more
sensitive
to
deactivation
by
ozone
–
Herpes,
Mumps,
Measles,
Influenza,
Rabies,
HIV
and
the
Chronic
Fatigue
producing viruses: Epstein Barr, Coxsackie and Cytomegalovirus.
2.- Stimulation of oxygen metabolism
Ozone
causes
increased
metabolism
inside
the
red
blood
cells
[increased
2,3-DPG],
which
releases
more
oxygen
to
the
tissues.
Ozone
also
stimulates
the
production
of
enzymes,
which
act
as
cell
wall
protectors
and
scavengers
of
free
radicals.
It
enhances
energy
production in the cells by complex biochemical reactions.
3.- Formation of Peroxides
When
ozone
is
introduced
into
the
body,
it
is
broken
down
into
free
radical
agents
called
peroxides.
These
have
beneficial
effects
because
they
are
attracted
to
weakened
or
diseased
cells
and
react
with
lipids
[fats]
in
the
cell
membrane.
The
enzymes
in
the
healthy,
intact
cell
wall
prevent
penetration
by
these
peroxides.
Thus
the
peroxides
in
ozone
selectively
attack
only
those
cells
which
contain
parasites,
viruses etc, or are weakened by cancer or toxins.
4.- Enhancement of circulation
In
circulatory
disease,
a
clumping
of
red
blood
cells
hinders
blood
flow
through
the
small
capillaries
and
decreases
oxygen
uptake
by
the
red
blood
cells
due
to
reduced
surface
area.
Ozone
reduces
or
eliminates
clumping,
and
restores
flexibility
thereby
increasing
oxygen
carrying
capacity.
Improved
viscosity
of
the
blood
also
leads
to better oxygenation of the tissues.
Ozone
oxidises
the
plaque
in
arteries,
which
unclogs
and
frees
up
the
circulation.
A
vasodilator,
Prostacycline,
is
also
produced
by
ozone,
which dilates the arteries.
5.- Dissolution of tumours
Ozone
inhibits
cancer
cell
metabolism.
In
addition,
ozone
oxidises
the outer lipid layer of cancer cells, thus destroying them.
6.- Activation of the immune system
Optimal
administration
of
medical
ozone
causes
an
increase
in
the
production
of
interferon
and
interleukins,
which
launch
an
entire
cascade of immunological reactions.
7.- Effect on medicines
The
potency
of
any
medicine
taken
concurrently
with
ozone
treatment
is
greatly
increased.
The
unpleasant
side
effects
of
toxic,
but
necessary,
medications
such
as
chemotherapy
can
be
greatly
minimised by ozone therapy.
WHAT CAN OZONE DO?
Inactivates viruses, bacteria, yeasts, fungi and protozoa
Stimulates the immune system
Improves circulation, clearing arteries and veins
Purifies blood and lymph
Normalizes hormone and enzyme production
Reduces inflammation
Reduces pain and calms the nerves
Prevents stroke damage
Improves cardiac arrhythmias
Improves brain function and memory
Oxidises toxins, allowing their excretion
Chelates heavy metals
Prevents and reverses degenerative disease
Prevents and treats communicable diseases
Prevents and treats Autoimmune disease
Increases
the
potency
and
minimizes
the
side
effects
of
chemotherapy
Assist
in
treatment
of
cancers,
post
viral
Chronic
Fatigue
Syndromes, Autism, etc.
FIELDS OF APPLICATION. INDICATIONS
Surgery
Abscesses,
wound
infection,
septic
conditions,
peritonitis,
decubitis,
burns,
badly
healing
wounds,
trophic
ulcers,
chronic
osteomyelitis,
thrombophlebitis,
arterial
occlusive
disturbances
of
the
lower
limbs,
diabetic
foot,
purulent-destructive
lung
&
pleura
diseases,
purulent
arthritis,
deformating
arthrosis,
cardio-surgical
interferences,
pre-
and postoperative treatment.
Internal medicine
Chronic
gastritis
&
gastroduodenitis,
chronic
colitis,
peptic
ulcer,
chronic
hepatitis,
hepatocirrhosis,
chronic
bronchitis,
bronchial
asthma,
rheumatic
diseases,
arthritis
&
arthrosis,
ischemic
heart
disease, allergic diseases, diabetes mellitus
Urology
Chronic
pyelonephritis,
acute
and
chronic
renal
failure
(nephrism),
cystitis, diseases transmissible by sexual way, urethritis, prostatitis
Neurology
Ischemic
apoplectic
attack,
cerebrovascular
insufficiency,
diseases
of
peripheral
nervous
system,
migraine,
disseminated
sclerosis,
compressive ischemic neuropathies, spinal osteochondrosis
Obstetrics & Gynecology
Inflammatory
female
genital
diseases,
bacterial
vaginosis,
vulvar
dystrophy,
gestosis,
early
toxicosis,
fetoplacental
insufficiency,
pregnancy
anemia,
spontaneous
&
threatened
abortion,
prevention
of
intrauterine
fetus
infection,
fatness-associated
pregnancy
complications, infertility
Dermatology
Furunculosis,
pyoderma,
herpes,
mycosis,
scleroderma,
psoriasis,
neurodermatitis,
eczema,
bullous
dermatosis,
acne,
allergodermia,
agiitis, lichen planus, pemphigus etc.
Cosmetology
Acne
rash,
cellulites,
local
lipodystrophy,
alopecia,
vascular
defects,
hypertrophic & keloid scars, age related changes
Dentistry
Caries
lesions,
hypersensitive
teeth,
cracked
tooth
syndrome,
peri-
apical
lesions,
gingival
&
periodontal
diseases,
post-extraction,
post-
extraction
alveolitis,
surgical
procedures,
peri-implantitis,
soft-tissue
lesions etc.
Ophthalmology
Blepharitis,
pain
syndrome,
eversion
of
the
eyelid,
glaucoma,
ischemia
of
the
eye
ground,
cataract,
keratitis,
conjunctivitis,
pemphigus,
erosion
of
the
cornea,
ulcers
of
the
retina,
hordeolum
etc.
HOW IS IT ADMINISTERED?
1.- Intravenous therapy
An
intravenous
line
is
inserted
into
a
vein,
and
100-150ml
of
blood
is
drawn
into
a
sterile
vacuum
flask.
Medical
ozone
is
also
inserted
into
the
flask
and
when
the
two
are
rapidly
mixed
together,
the
blood
turns
a
bright
cherry
red.
This
ozonated
blood
is
now
highly
charged
with
oxygenating
power,
and
fed
back
into
the
same
vein.
The
whole
procedure takes about 30 minutes.
2.- Vaginal, urethral or rectal insufflations
Ozone
is
introduced
into
the
vagina,
urethra
or
rectum
by
means
of
a
catheter.
3.- Autohaemotherapy
5-10
ml
blood
is
withdrawn
by
syringe,
mixed
with
ozone,
and
injected back into a deep muscle.
4.- External limb bagging
A
limb
is
covered
with
an
airtight
bag
and
ozone
is
introduced
into
the bag for 30-40 minutes.
5.- Ozonated olive oil
Ozone
is
bubbled
through
olive
oil
continuously
for
7
days.
The
resulting
cream
is
very
effective
as
a
topical
application
in
a
wide
variety of skin conditions.
6.-
Intramuscular,
Intra-articular
&
intradiscal
O2/O3
gas
injections.
ARE THERE ANY PRECAUTIONS TO OBSERVE?
To
prevent
any
unwanted
oxidative
effects,
it
is
best
to
take
a
good
anti-oxidant
combination
for
7
days
before
starting
intravenous
ozone therapy.
Ozone therapy
is contraindicated
in the following:
Acute
myocardial
infarction,
severe
cardiovascular
instability
(block,
Wolff-Parkinson-White),
convulsive
status,
pregnancy,
recent
internal
bleeding
and
blood
coagulation
disorder,
severe
anemia,
hyperthyroidism,
thrombocytopenia,
cramp
tendency,
ozone
allergy,
chronic
relapsing
pancreatitis,
alcoholic
intoxication
and
Fauvism
(a
deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase).
References
Bocci,
V.
2002.
Oxygen-Ozone
Therapy.
A
Critical
Evaluation.
Kluwer Academic Pub.
Bocci, V. 2005. Ozone, A new medical drug. Springer
Viehban-Haensler,
R.
2002.
The
Use
of
Ozone
in
Medicine.
4th
Ed. ODREI-Pub.
Viebahn-Hänsler,
R.
Ozon-Sauerstoff-Therapie.
Editorial
Haug.
2009.
Viebahn-Hänsler
R.
Hitos
del
ozono
médico.
Revista
de
la
Sociedad Española del Dolor. Vol. 12. II. Editorial ARAN. 2005. 3-9.
Menéndez
Cepero
S.
A,
González
Álvarez
Ricardo,
Ledea
Lozano
O.E.
et
al.
Ozono:
Aspectos
básicos
y
aplicaciones
clínicas.
Editorial
CENIC.2008.
Rovira
G.
La
Ozonoterapia
tópica
en
el
manejo
de
úlceras
flebostáticas
dolorosas
de
más
de
seis
meses
de
evolución.
Rev.
Soc.
Esp. Dolor 12: Nº Extra II, 48-52, 2005.
De
Lucas
J.C.
Infiltración
periférica
con
ozono.
Indicaciones,
técnicas
y
experiencia
clínica.
Revista
de
la
Sociedad
Española
del
Dolor. Vol.12.II. Editorial ARAN. 2005. 37-47.
Hidalgo
Tallón
F.J.
Oxígeno-ozonoterapia:
una
realidad
médica.
Revista
de
la
Sociedad
Española
del
Dolor.
Vol.16.
3.
Editorial
ARAN.
2009. 190-191.
Andreula
C.,
Simonetti
L.,
et
al:
Minimally
Invasive
Oxygen-
Ozone
Therapy
for
Lumbar
Disk
Herniation.
AJNR
Am
J
Neuroradiol
24: 996-1000, May 2003.
Baeza
J.
Infiltración
neuroaxial
con
ozono.
Fisiopatología
y
mecanismos
de
acción.
Revista
de
la
Sociedad
Española
del
Dolor.
Vol.12. II. Editorial ARAN.2005. 18-23.
Bocci
V.
Mecanismos
de
acción
generales
de
la
ozonoterapia
y
mecanismos
en
el
tratamiento
del
dolor.
Revista
de
la
Sociedad
Española del Dolor. Vol.12. II. Editorial ARAN. 2005.24-36.
Borrelli
e.,
Bocci
V.
A
Novel
Therapeutic
Option
for
Crhonic
Fatigue
Syndrome
and
Fibromyalgia.
Riv
Ital
Ossigeno-Ozonoterapia
1: 149-153, 2002
If
you
would
like
additional
information
regarding
our
services
or to request an appointment, you can contact us by phone
(952 80 53 68) or by
email
.